|
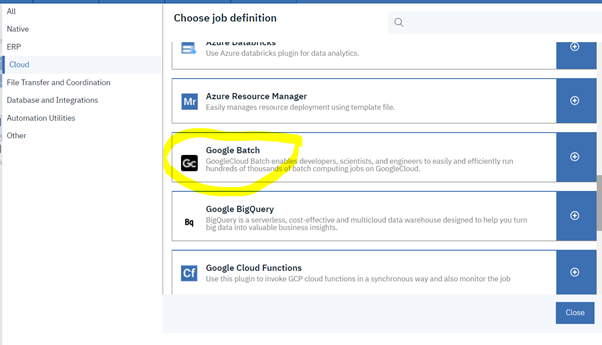
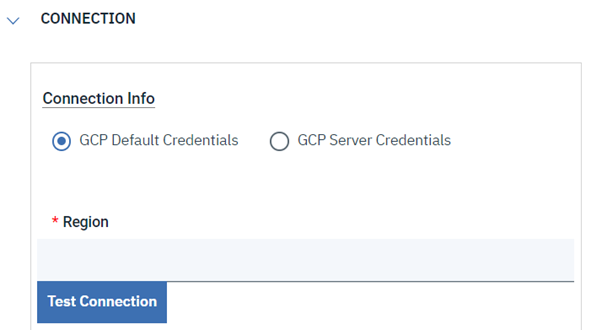
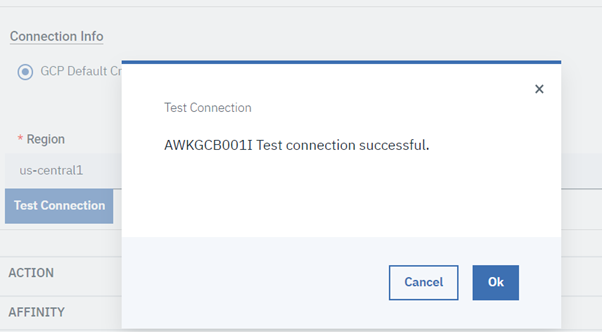
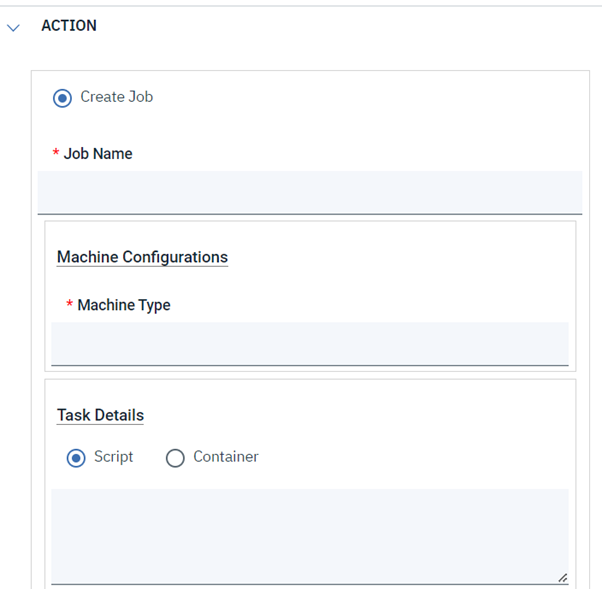
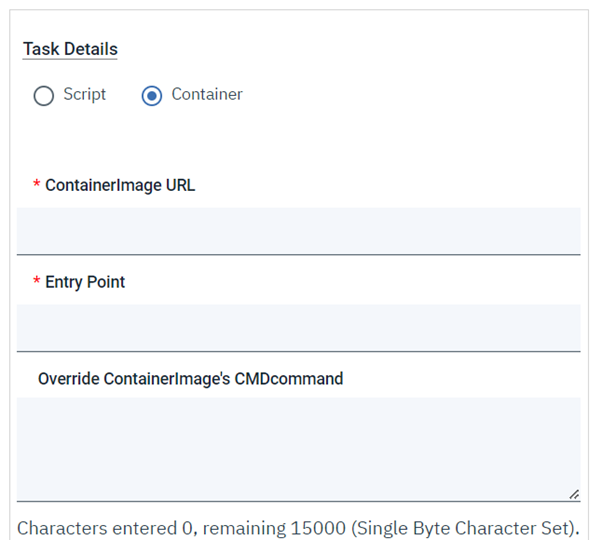
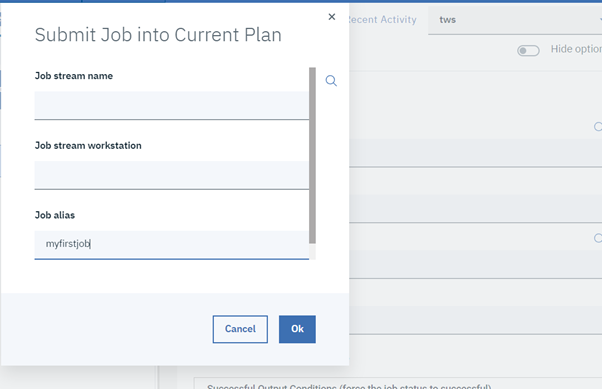
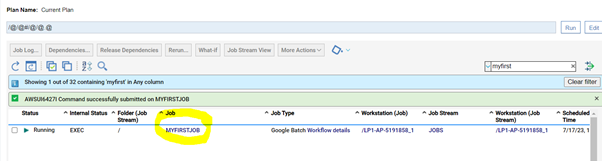
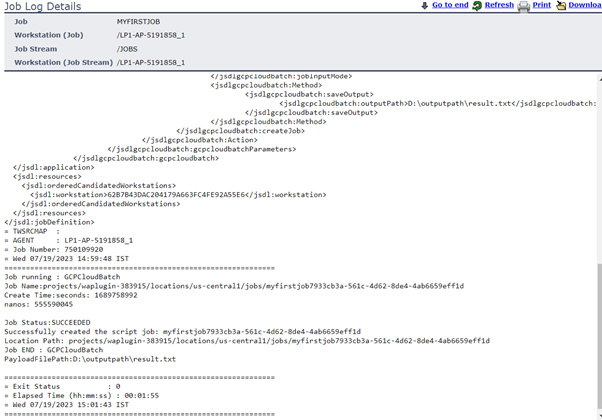
Let's start understanding Google Batch, and then go forward to discovering the GCP Batch plug-in and the benefits of using it. Google Batch is a fully managed service that lets you schedule, queue, and execute batch processing workloads on Google Cloud resources. Using Batch, we don't need to configure and manage third-party job schedulers, provision and deprovision resources, or request resources one zone at a time. To run a job, you specify parameters for the resources required for your workload, then Batch obtains resources and queues the job for execution. Batch provides native integration with other Google Cloud services to aid in the scheduling, execution, storage, and analysis of batch jobs, so you can focus on submitting a job and consuming the results. Thus, to empower your Workload Automation environment, download the Google Batch plug-in available on Automation Hub. After downloading it, log in to the Dynamic Workload Console and go to the Workload Designer. Create a new job and select “Google Batch” in the Cloud section. Connection To begin, connect to the Google Cloud server. To connect to Google Cloud, you have two options under the Connection tab: 1. GCP Default Credentials: If the VM is already located within the GCP environment, you can select this option since no explicit credentials are required. 2. GCP Server Credentials: By choosing this option, you can manually enter the project ID and the GCS account. (a unique name associated with each project). After that, choosing Test Connection, you can check your Google Cloud connection. ActionUse this section to define options for GCP cloud batch function. You can choose to make a batch using a script or container, delete an existing job, or both. To create a job, you have two options. Create a job using script. Create a job using container. Create Job You can select the "Create Job" to create a job, Job Name Enter the Job name. Machine Configuration Machine type- Machine Type must be defined in Google Cloud Batch Machines which are defined in Google Cloud Batch documentation. Task details Script You can see the text area where you can input the script once you choose the "Script" radio button, provided that all relevant fields are enabled. while keeping the Container task's associated fields enabled. Task Count Enter the total number of tasks. Must be a whole number between 1 and 10,000. Task Parallelism Enter the number of tasks you want running at the same time. Must be a whole number between 1 and 1,000. Task VCPUs Enter between 0.5 and 224 vCPUs Task Memory Enter between 0.5 and 896 GB Note: Job name, Machine type, taskCount, taskParallelism, task CPUs, task and Memory fields are mandatory fields Container You can select the "Container" radio button to enable all the required fields, while keeping the fields related to the Script task disabled. Containerimage URL Enter your image URL from a public registry or use a private image hosted on the Google Container Registry. Entry Point Specify the command that have to run instead of your container's entrypoint command. Containterimage command Enter the command to be run in place of the CMD command for your container image. Note: It is not recommended to specify "zero" in the TaskCount, TaskParallelism, Task CPUs, or TtaskMemory columns. Save Function Output to File Select the check box to save the function output. Output File Path Provide the location to save the function output files. Submitting your job Now, it is time to submit the job in the current plan. Add the job to the job stream that automates your business process flow. Select the action menu in the top-left corner of the job definition panel and click Submit Job into Current Plan. A confirmation message is displayed, and you can switch to the Monitoring view to see what is going on. Monitor Page JOB Log: Author Co-author
0 Comments
Your comment will be posted after it is approved.
Leave a Reply. |
Archives
July 2024
Categories
All
|





 RSS Feed
RSS Feed