|
During the years, many features have been developed involving more and more complex analysis and actions in the Current Plan modifications due to ad hoc requests. At the same time customer’s daily workload increased in size and complexity, becoming more dependent on ad hoc actions (ETT processing, Automatic recovery actions etc.) Storage consuming also increased, so that we delivered via SPE (930 and 950) the possibility to use a Data Space dedicated to MCP actions. This led for a need to do some changes to guarantee the usual efficiency of the product in processing a big amount of modify current plan actions. With APAR PH10775 (TWS for z/OS 930) and PH12637 (ZWS 950) changes in MCP code lead to a big performance improvement in executing modify current plan actions. The situations in which the benefits are bigger are:
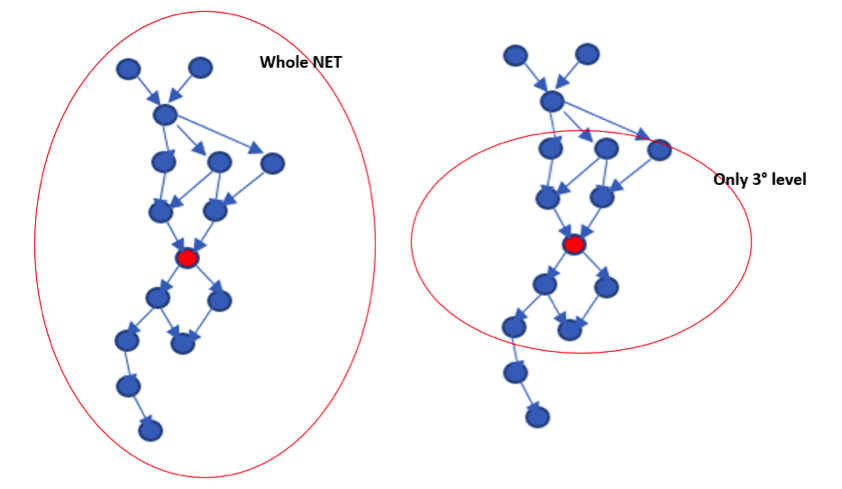
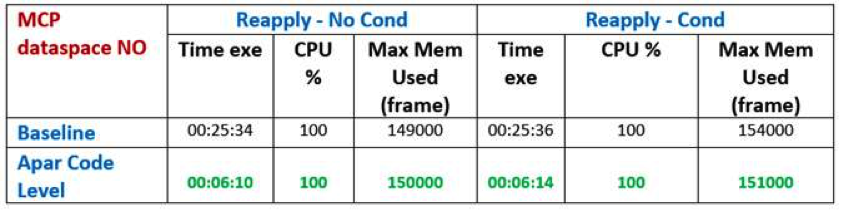
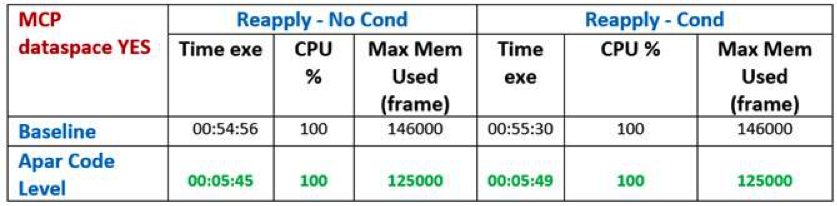
This was obtained by improving internal algorithm, reducing to the strictly needed writing on MCP data space, and reducing the amount of Network to be loaded when a modify current plan action must be done. For “Network” we mean the set of occurrence and operation blocks that are connected to the occurrence/operation subject of the change and that are loaded into the storage to execute the action because they are related by dependencies (successors and predecessors of different levels). Not all the changes have the same level of complexity, so not all the changes need the whole predecessor/successor network loaded. A complex change is a change that may have impact on data and status of predecessors and successors at different levels. The APAR worked in this direction: it reduced the Network to the minimum when this was possible considering the complexity of the change. A change is complex when predecessors and successor (at different levels) of the main changed operation can have their status or data changed too. The benefit of the APAR can be seen for example from the picture below, reporting the elapsed time needed to re-apply JT events results one of the tests we did. The conditions of this specific test were the following:
With MCP Data space not involved, the improvement in this specific test was from about 25 minutes to about 6 minutes, that is about a 76% improvement. With MCP Data space involved, the improvement in this specific test was from about 55 minutes to about 6 minutes, that is about an 89% improvement. Obviously, the benefit depends on the kind and size of network involved. In general we can say that the larger the size and complexity the greater the benefit. Rossella Donadeo
Technical leader of Workload Scheduler for z/OS. Rossella graduated with a bachelors degree in mathematics in 1982. She is the Technical leader of Workload Scheduler for z/OS. Rossella worked for a couple of years in a small software house, and then in 1984 joined IBM. Since then she worked in level 3, development and verification. From 1996 she has been focused on Workload Scheduler for z/OS product. She successfully led the development of ZWS 950. Rossella is a Mindfulness instructor, fond of trekking, yoga, cooking and practices Vipassana meditation. She is also a writer and had a book published.
0 Comments
Your comment will be posted after it is approved.
Leave a Reply. |
Archives
July 2024
Categories
All
|

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed